
People who commit self immolation for humanitarian reasons are not mentally disturbed, crazy and psychopaths. In fact they deserve an enormous amount of respect because they actually Feel Immense Passion and Anger about the injustices they have personally experienced and/or their people. They harm no one except themselves, pursuing one of the most painful and prolonged methods of death. All, to expose and increase awareness about reality, the plight of people and to alleviate the suffering of those who can not protest and represent themselves.
Those who pursue Self Immolation, know Actions Speak Far Louder and More Honestly than Words. These people are not driven by Money, Materialism and Greed unlike some Politicians and Exhibitionists, who Feel only for themselves.
CENSORSHIP
Unfortunately there are Names and Self Immolation Stories missing from my list. Governments and the media have censored details. While suicide bombers receive maximum media attention and coverage, those who only harm themselves, even For The Same Reasons as Suicide Bombers, are ignored. This is concrete proof and a sad indication of what supposed Human Rights Respecting Governments actually prefer and want: the carnage and injury of tens, hundreds and thousands of innocent people for reasons of shock, awe and fear, which they then can use to manipulate and utilize for their own political and economic agendas, globally. Of course 9/11 and other MCIs are simple demonstrations of this fact.
IT CHANGES NOTHING. - IT CHANGES EVERYTHING!
Some people will claim self immolation is an unsuccessful method of changing anything. It may not change governments and the UN, but it will certainly motivate and influence many other people to take a more defiant stand and to take action themselves. If a human being genuinely feels strongly about any cause, words and theatrical speeches in public are not evidence; the proof of the depth of anyone's convictions and soul, lies in their deeds.
THICH QUANG DUC - A SHINING LIGHT
An Inspiration and Shining Light for Many Self Immolations has been Thich Quang Duc, a Vietnamese Buddhist monk who committed Self Immolation on 11 June 1963. He wanted to stop the persecution of Buddhists by South Vietnam's Ngo Dinh Diem administration, without using violence and causing harm to anyone else.
On the evening of Thursday 12 February 2009, a 26-year-old Sri Lankan protester poured gasoline over himself and burned to death outside the U.N. complex in the Place des Nations, Geneva, Switzerland. Murugathasan was a Computing graduate living in London.
A few meters away from Murugathasan's burning body, the police found a letter typed in Tamil and English explaining why he had chosen to die: "We Tamils, displaced and all over the world, loudly raised our problems and asked for help before [the] international community in your own language for three decades. But nothing happened ... So I decided to sacrifice my life ... The flames over my body will be a torch to guide you through the liberation path."
Several hours earlier, about 500 Tamils had demonstrated on the square to protest Sri Lanka's military action against ethnic Tamils. The Sri Lankan government is fighting to crush the rebels and end their 25-year campaign for an independent homeland for the country's ethnic minority Tamils, who have suffered marginalization under the country's majority ethnic Sinhalese. More than 70,000 people have been killed in the violence.
Seven Tamils - including Murugathasan - have burned themselves to death in the past month to protest about the treatment of their people by Sri Lanka's Sinhalese government. Most were in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, but on 14 February, another British-based Tamil allegedly tried to set himself on fire outside Downing Street, but was arrested before he could do so.
Links: The Guardian Newspaper (UK) / IHT Newspaper
RAMIRO GUILLEN TAPIA (Xalapa, Mexico)

On 1 October 2008, the indigenous Mexican leader Ramiro Guillén Tapia, aged 65, attempted self-immolation during an act of protest against the local government in the city of Xalapa, Veracruz, Mexico. He died of heart failure the next day, after suffering third-degree burns over 70 percent of his body.
Ramiro Guillén Tapia was the chairman of the Sierra de Soteapan Human Rights Commission. The act of self-immolation was to protest authorities' refusal to award some disputed lands to his community in the Soteapan Mountains.
Links: Fox News (US) / TheNews.Co.Mx (Mexico)

Heo Se-Uk was a 54-year-old South Korean labor union member and taxi driver who set himself ablaze on 1 April 2007 in Seoul to protest the U.S.-Korea Free Trade Agreement. He lived for two weeks after the incident, despite serious burns on 63% of his body.
 He finally succumbed to a septic infection on 15 April 2007.
He finally succumbed to a septic infection on 15 April 2007.Link: Heo Seuk Wiki

Uddhav was a Nepali asylum seeker who died after setting fire to himself at the Eagle Building in Glasgow, Scotland on 7 March 2007, prior to his immigration hearing. He died on 19 March 2007. A former police officer, he was afraid of being deported to Nepal after exposing corruption within the police force.
Links: Uddhav Bhandari Wiki / The Himalayan Times / The Herald (Scotland)
 Malachi (Mark David) Ritscher was a Chicago musician and anti-war protestor who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest against the War in Iraq. Ritscher's self-immolation took place on the side of the Kennedy Expressway near downtown Chicago during the morning rush hour of Friday 3 November 2006.
Malachi (Mark David) Ritscher was a Chicago musician and anti-war protestor who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest against the War in Iraq. Ritscher's self-immolation took place on the side of the Kennedy Expressway near downtown Chicago during the morning rush hour of Friday 3 November 2006.In a suicide letter published on his website (http://www.savagesound.com/gallery99.htm), he described at length his political convictions as to the Iraq War and his choice to take his own life:
"My actions should be self-explanatory, and since in our self-obsessed culture words seldom match the deed, writing a mission statement would seem questionable. So judge me by my actions. Maybe some will be scared enough to wake from their walking dream state - am I therefore a martyr or terrorist? I would prefer to be thought of as a 'spiritual warrior'. Our so-called leaders are the real terrorists in the world today, responsible for more deaths than Osama bin Laden."
"if I am required to pay for your barbaric war, I choose not to live in your world."
Link: Malachi Ritscher Wiki
Roland Weisselberg (4 July 1933 – 31 October 2006) was a retired Lutheran Vicar who received public attention by his self-immolation in a German monastery. A critic of the rulers of the German Democratic Republic, he retired in 1989 because of his state of health. After the German reunification he was worried about the weakness of Christianity in East Germany and about Islam, whose rise was, as he believed, furthered by the "ambiguity of the church". Weisselberg set fire to himself in the Erfurt monastery (where Martin Luther took his monastic vows in 1505), shouting repeatedly "Jesus" and "Oscar" (referring to Oskar Brüsewitz).
Link: Roland Weisselberg Wiki
Eleftheriya was a Greek who committed self immolation in Sepolia, Athens, in order to highlight the treatment of the Kurds in Turkey. Fortulaki had a Kurdish partner, with whom she had two children. She died on 28 March 2006.
Link: Eleftheriya Fortulaki Wiki
 On Tuesday 24 June 2003, Neda Hassani, aged 26, set herself on fire in front of the French Embassy in Great Britain to demand the release of Maryam Rajavi and 150 of her supporters, after a French crackdown on the People's Mujahedeen of Iran, also known as Mujahedeen Khalq Organization (MKO). It has fought an armed campaign for the past 20 years to overthrow the religious rulers of Iran. The French government had accused the MKO of plotting terrorist attacks against Iran.
On Tuesday 24 June 2003, Neda Hassani, aged 26, set herself on fire in front of the French Embassy in Great Britain to demand the release of Maryam Rajavi and 150 of her supporters, after a French crackdown on the People's Mujahedeen of Iran, also known as Mujahedeen Khalq Organization (MKO). It has fought an armed campaign for the past 20 years to overthrow the religious rulers of Iran. The French government had accused the MKO of plotting terrorist attacks against Iran.Links: The Guardian Newspaper UK / Statement of David Kilgour Former Canadian Politician
On Sunday 2 September 2001, a man burned himself to death in Danang, Central Vietnam to protest against religious persecution by the Vietnam Communist Party and its government. Ho Tan Anh, aged 61, was an honest and devoted farmer, and leader of the Buddhist Youth Movement in Quang Nam Province. He set himself on fire at 4:30 AM and died shortly later at a park of the city.
Link: Ho Tan Anh
SHAHRAZ KAYANI (Canberra, Australia)

In April 2001, Shahraz Kayani, a Pakistani refugee settled in Australia set himself alight on the steps of Parliament House, Canberra. Dying days later in hospital, he was protesting against the refusal of the government to grant the entry of his wife and daughters into Australia, one of whom suffered from Cerebral Palsy.
Link: ABC Network (Australia)
In 2001, a group of people self-immolated in Tiananmen Square, Beijing, China. China Central Television broadcast the event nationally on Chinese new year and claimed the immolators were practitioners of the FALUN GONG. Falun Gong supporters claim it was a setup by the Chinese government.

(Born 1950 - 22 October 1996) Kathy was a West Philadelphian performance artist and activist who killed herself in an act of self-immolation on the University of Pennsylvania campus in 1996. She explained the rationale behind her suicide:
Links: Kathy Change Wiki / Official Kathy Change WebsiteI want to protest the present government and economic system and the cynicism and passivity of the people…as emphatically as I can. But primarily, I want to get publicity in order to draw attention to my proposal for immediate social transformation. To do this I plan to end my own life. The attention of the media is only caught by acts of violence. My moral principles prevent me from doing harm to anyone else or their property, so I must perform this act of violence against myself. . . . It is a waste of energy to get angry and gripe at the government. The government must be replaced with a truly democratic self-government of, for and by the people. Those working in industries essential to maintaining life should democratically take over their workplaces and organize an emergency economy to supply the needs of the people. The rest of the people should meet in their communities to organize a new directly democratic community-based self-government.
Link: Sabine Kratze Wiki
Reinhold was born in 1920 in the predominantly German inhabited and cultural Sudetenland, which now lies in the Czech Republic. He was a German Wehrmacht veteran and Diploma Chemist who poured gasoline over himself and committed suicide on 25 April 1995, on the steps of Munich's historical Feldherrnhalle, in protest against what he called "the ongoing official slander and demonization of the German People and German soldiers 50 years after the end of World War II". Twelve hours later, he died in a Munich hospital.
In a farewell letter, he wrote: "With my 75 years of age, all I can do is to set a final sign of contemplation with my death in flames. And if only one German comes to consciousness and finds his way to the truth, then my sacrifice will not have been in vain."
Link: Reinhold Elstner Wiki
DR. HOMA DARABI (Tehran, Iran)

Homa Darabi (January, 1940 - 21 February 1994) was a pediatrician from Iran licensed to practice medicine in New Jersey, New York, and California. She returned to Iran in 1976 to serve her country as a psychiatrist and after the Islamic Revolution, Islamic authorities shut down her office because she had refused to wear the hijab. On 21 February 1994, Darabi, a 54 year old mother of two daughters immolated herself in Tehran while shouting "Death to Tyranny! Long live freedom! Long live Iran!". Later, her sister Parvin Darabi named the Dr. Homa Darabi Foundation in her remembrance and co-authored with her son, a biography of Dr. Darabi, Rage Against the Veil.
Links: Dr Homa Darabi Foundation / Homa Darabi Wiki / Rage Against the Veil: The Courageous Life and Death of an Islamic Dissident Wiki
Bamford wrote that 'a photograph in the newspaper of a distressed little Balkan girl about the age of my own daughter galvanised me into action'. A few days later he wrote a final message: 'The British army must not be a guard of honour at a mass funeral. Bosnian babies, children, and womenfolk are waiting for the politicians to do what they know they should - give them military protection.'
A film about Graham Bamford, his actions, the silence built up around them, and also about the filmmaker and his effort to produce a film about the event are available here:
Link: Film About Graham Bamford "Graham and I"
Chan I-Hua was a Taiwanese pro-democracy activist. He performed self-immolation on 19 May 1989 when the funeral procession of fellow activist Cheng Nan-jung (who had similarly immolated himself) was blocked by the police in front of the Presidential Office Building in Taipei.
Link: Chan I-Hua Wiki
CHENG NAN-JUNG (Taiwan)
Cheng Nan-Jung (born 12 September 1947 in Taipei and died 7 April 1989) was a Taiwanese publisher and pro-democracy activist. He was the founder of the Freedom Era Weekly. He is known internationally for setting himself on fire to voice for Taiwanese independence.
In 1989, Cheng was charged with insurrection for printing a new Constitution for the Republic of Taiwan. An arrest warrant was issued. He refused to appear in court. When the police arrived to arrest him on 7 April, he committed suicide by self-immolation. He set fire to the building and died in the blaze. At Cheng's funeral on 19 May, another Taiwanese pro-democracy activist, Chan I-hua, also immolated himself when the funeral procession was blocked by police.
Link: Cheng Nan-Jung Wiki
Liviu Cornel Babeş (January 19, 1942 – March 2, 1989) was a Romanian electrician and painter who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest. On 2 March 1989, Babeş died after setting himself on fire on the Bradu ski slope at Poiana Braşov in sign of protest against the communist regime. He left a message: „Stop Mörder! Braşov = Auschwitz”. In Romania, according to Law no. 93/June 3, 1997 Liviu Cornel Babeş is a hero.
Link: Liviu Cornel Babes Wiki
Sebastian Acevedo was a Chilean miner who committed self-immolation on 11 November 1983 as a protest against the detention of his children by the Chilean police during the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet.
Following a protest in the city of Concepcion, Acevedo's children Candelaria and Galo Fernando are arrested. Their father searches for them, but at each police station officials deny any knowledge of their whereabouts. In despair, Acevedo plants himself at the Cathedral entrance, shouting "Give me back my children!" Pleading that the CNI not torture his children, Acevedo pours gasoline over his clothing, and threatens to set himself on fire. A uniformed policeman attempts to disperse the crowd that has gathered, challenging him to carry out his threat. In an instant, Acevedo strikes a match, his body igniting like a torch. He dies that same day, after learning that Candelaria has been released.
The agonizing image of 50 year-old Sebastian Acevedo, captured by a photographer, stuns the world. His act of bravery and devotion inspires the birth of a non-violent protest movement two months later. Led by priest Jose Aldunate, the Sebastian Acevedo Anti-Torture Movement becomes a broad-based organization that challenges the practice of torture.
Link: The Guardian Newspaper
ARTIN PENIK (Istanbul, Turkey)

Artin Penik (Died 15 August 1982) was a Turkish-Armenian who set himself on fire in protest of the terrorist attacks in Esenboğa International Airport by the Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia (ASALA, also known as Third October) on 10 August 1982. Artin, a 61-year-old self-employed tailor, set himself on fire in Taksim plaza, the main square of Istanbul, Turkey, after leaving a suicide note in which he wrote "I can no longer bear the grief over slayings of innocent people."
Links: Artin Penik Wiki / You Tube Video: The Last Words of Artin Penik (Turkish Audio/English Subtitles) / Turkish Journal Article
Link: Per-Axel Arosenius Wiki
OLEKSA MYKHAYLOVYCH HIRNYK (Kaniv, Ukraine)
In 2000 a guelder-rose bush was planted on the place of his death. By decree of the President of Ukraine on 18 January 2007 Oleksa Hirnyk was awarded the title of the Hero of Ukraine posthumously and awarded the Order of the State.
Link: Oleksa Hirnyk Wiki
Hartmut Gründler (11 January 1930 – 21 November 1977) was a German teacher from Tübingen, engaged in environmental protection. On November 16,1977 ( the Day of Prayer and Repentance) Gründler burned himself in Hamburg during the SPD Party Congress out of protest against "the continued governmental misinformation" in the Atomic policy of the German Federal Government, particularly concerning the permanent disposal of nuclear waste.
Link: Hartmut Grundler Wiki

Alain Escoffier (25 October 1949 – 10 February 1977) was a French anti-communist activist and martyr. He was a bank clerk and he had married an East-Germany refugee. He belonged to the right-wing Parti des forces nouvelles. On 10 February 1977, the thirtieth anniversary of the Treaty of Paris he self-immolated on the Champs-Élysées before the offices of Soviet airlines Aeroflot. He died crying "Communistes assassins" (Murderer Communists).
Link: Alain Escoffier Wiki

Oskar Brüsewitz ((Born 30 May 1929 – Died 22 August 1976) was an East German Lutheran pastor who committed self-immolation to protest the repression of religion in the Communist state of East Germany. On 18 August 1976 Brüsewitz committed suicide by self-immolation in a public market in front of the church in Zeitz. He died on 22 August 1976.
He was critical of the East German Communist regime imposed by the Soviet Union after the war and symbolic acts of protest, including the installation of a cross of neon lamps at his church, brought him to the attention of the authorities. The leadership of his church sided with the state, rather than its priest, and asked, in 1976, for Brüsewitz to be moved to another rectorate. This was the immediate trigger for his suicidal protest.
The Communist authorities initially attempted to suppress news of the event then, when news leaked and public support for his action grew, they branded him a psychopath(!). On 31 August Neues Deutschland, the official newspaper of the SED (Socialist Unity Party of Germany), printed an article entitled „Du sollst nicht falsch Zeugnis reden“ "You shall not bear false witness" which asserted that self-immolation was the action of a sick, crazy man. 30 Years later, on the anniversary of his death, Neues Deutschland wrote an apology for the article they had carried at the time, admitting that the piece had been "slanderous" and written, not by journalists, but in one of the many offices of the central committee of the SED.
Link: Oskar Brüsewitz Wiki
Romas Kalanta (22 February 1953 - 14 May 1972) was a Lithuanian known for his self-immolation for political reasons. Romas Kalanta set himself on fire in the square adjoining the Laisves Aleja in front of the Kaunas Musical Theatre in the Lithuanian city of Kaunas on 14 May 1972 in protest of the occupation of Lithuania and the oppression of the Lithuanian language, culture and people by the government of the Soviet Union.
Link: Romas Kalanta Wiki
Link: Joseba Elosegi Wiki

Kostas Georgakis (23 August 1948 Corfu, Greece – 19 September 1970 Genoa, Italy), was a Greek student of Geology, who set himself ablaze in Genoa, Italy as a protest against the Greek military junta of 1967-1974. Georgakis is considered the precursor of the later student protests, such as the Polytechnic uprising. At the time, his death caused a sensation in Greece and abroad as it was the first tangible manifestation of the depth of resistance against the junta.
His last words were: Long Live Free Greece.
Link: Kostas Georgakis Wiki
George Winne Junior (Born 1947 – Died 11 May 1970) is remembered as a protester of the Vietnam War who set himself on fire in a deliberate act of self-immolation in Revelle Plaza on the campus of the University of California, San Diego on 10 May 1970, to protest the United States involvement in the war. He died ten hours later, asking his mother to write a letter to President Nixon.
His last words were "I believe in God and the hereafter and I will see you there."
Link: George Winne Wiki
The wave of suicide attempts by immolation that ran through the Czech lands in the first months of 1969 was a unique event on a world-wide scale, a result of the social atmosphere at the time. After Jan Palach, 26 people attempted suicide between January 20, 1969 and the end of April including: On 22 January 1969 - Miroslav Malinka set himself on fire and Blanka Nachazelova suffocated herself with coal gas. Josef Hlavaty burned himself alive and died on 25 January 1969.
Link: Czech Radio
 Evžen Plocek (29 October 1929 – 9 April 1969) was a Czech man (reform communist) who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest. Plocek died after setting himself on fire in Main Square in Jihlava, Czechoslovakia on Good Friday, 4 April 1969 in protest.
Evžen Plocek (29 October 1929 – 9 April 1969) was a Czech man (reform communist) who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest. Plocek died after setting himself on fire in Main Square in Jihlava, Czechoslovakia on Good Friday, 4 April 1969 in protest.Just before his feat he dropped a paper with the text: "Truth is revolutionary - wrote Antonio Gramsci" and "I am for a human face - I can't stand the unfeeling ones - Evžen".
In spite of a number of difficulties, the workers at Motorpal were able to hold a public funeral in Jihlava. Not a word of Evžen Plocek's self-immolation made it into the central press, however.
Link: Plocek Czech Radio Archive
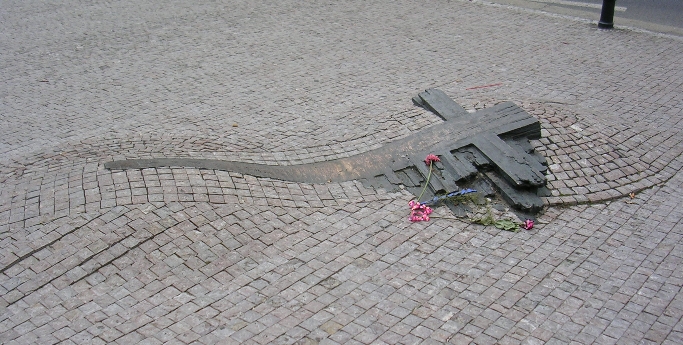 Picture: The memorial to Jan Palach and Jan Zajíc in front of the National Museum, Prague, Czech Republic. There are several other memorials to Palach in cities throughout Europe, including a small memorial inside the glacier tunnels beneath the Jungfraujoch in Switzerland.
Picture: The memorial to Jan Palach and Jan Zajíc in front of the National Museum, Prague, Czech Republic. There are several other memorials to Palach in cities throughout Europe, including a small memorial inside the glacier tunnels beneath the Jungfraujoch in Switzerland.  Jan Zajíc (3 July 1950-25 February 1969) was a Czech student who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest. He was a student at the technical college, specializing in railroads, and was also interested in poetry and humanities. In 1969 he took part in a hunger strike and a commemoration ceremony by students for Jan Palach near the statue of Saint Wenceslas in Prague. It was probably this event which planted the idea of becoming Palach's successor in Zajíc's mind.
Jan Zajíc (3 July 1950-25 February 1969) was a Czech student who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest. He was a student at the technical college, specializing in railroads, and was also interested in poetry and humanities. In 1969 he took part in a hunger strike and a commemoration ceremony by students for Jan Palach near the statue of Saint Wenceslas in Prague. It was probably this event which planted the idea of becoming Palach's successor in Zajíc's mind.Link: Jan Zajic Czech Radio
*
JAN PALACH (Prague, Czechoslovakia)

Jan Palach was a Czech student who committed suicide by self-immolation as a political protest against the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968. Palach died after setting himself on fire in Wenceslas Square in Prague, Czechoslovakia on 16 January 1969 in protest. The funeral of Palach turned into a major protest against the occupation.
After the Velvet Revolution, Palach (along with Zajíc) was commemorated in Prague by a bronze cross embedded at the spot (shown above) where he fell outside the National Museum, as well as a square named in his honour.
Links: Jan Palach Wiki / Jan Palach Czech Radio

Ryszard Siwiec (Born 1909— Died 12 September 1968) was a Polish accountant, teacher and former Home Army soldier who was the first person to set himself on fire in protest against the Soviet-led invasion of Czechoslovakia. A father of five from Przemyśl, Siwiec planned his self-immolation in advance, leaving written and tape-recorded statements explaining his revulsion at both the Warsaw Pact invasion and communist Poland's participation in it.
He set himself ablaze in Warsaw during a national harvest festival on 8 September 1968 at the Dziesięciolecia Stadium, and died in hospital four days later. His act was witnessed by nearly 100,000 spectators, including the national leadership and foreign diplomats who had been invited to the festival intended as a vast propaganda spectacle.
Orders (posthumous)
- Order of Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, first class, awarded in 2001 by Václav Havel, President of the Czech Republic.
- Order of Polonia Restituta, Commander's Cross, awarded in 2003 by Aleksander Kwaśniewski, President of Poland. Because of Aleksander Kwaśniewski's past as communist dignitary, Ryszard Siwiec's family refused to accept the award.
- Order of the White Double Cross, awarded in 2006 by Ivan Gašparovič, President of Slovakia
Links: YouTube Film Footage of Ryszard Siwiec, Self Immolation (Polish Audio/English Subtitles) / Ryszard Siwiec Wiki / Prague Street Renamed In Honour Of Polish "Human Torch" Against Soviet Invasion (13 Feb 2009) / Polish National Stadium in the Name of a Hero? (24 Feb 2009)
Link: Florence Beaumont Wiki
At the time, he was a 22-year old Catholic Worker Movement member. La Porte died the next day from second and third-degree burns covering 95 percent of his body. Despite his burns, he remained conscious and able to speak. When asked why he had burned himself, La Porte calmly replied, "I'm a Catholic Worker. I'm against war, all wars. I did this as a religious action."
Link: Roger Allen LaPorte Wiki

Norman Morrison (29 December 1933 - 2 November 1965), born in Erie, Pennsylvania, was a Baltimore Quaker best known for committing suicide in an act of self-immolation to protest United States involvement in the Vietnam War. On 2 November 1965, Morrison doused himself in kerosene and set himself on fire below Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara's Pentagon office. Morrison took his daughter Emily, then one year of age, to the Pentagon, and either set her down or handed her off to someone in the crowd before setting himself ablaze.
Link: Norman Morrison Wiki / Norman Morrison, Deed of Life, Deed of Death By Anne Morrison Welsh, Winds of Peace 1998 (PDF) PP4-7 / Norman Morrison Information
HUH JIK (South Korea)
Alice Herz (Born 1883 – Died 26 March 1965) was an elderly Quaker and the first activist in the United States known to have immolated themself in protest of the escalating Vietnam War, following the example of Buddhist monk Thich Quang Duc. A longtime peace activist, she attempted self-immolation on 16 March 1965, in Detroit, Michigan, at the age of 82. A man and his two boys were driving by and saw her burning and put out the flames. She died of her wounds ten days later.
Confiding to a friend before her death, Herz remarked that she had used all of the accepted protest methods available to activists--including marching, protesting, and writing countless articles and letters--and she wondered what else she could do. Self-immolation was her final act of protest, in a democratic country.
Links: Alice Herz Wiki / Google Book: Phoenix: Letters and Documents of Alice Herz : the Thought and Practice of a Modern-Day Martyr By Alice Herz, Shingo Shibata
*

Thich Quang Duc died on 11 June 1963 and was a Vietnamese Mahayana Buddhist monk who burned himself to death at a busy Saigon road intersection. He was protesting the persecution of Buddhists by South Vietnam's Ngo Dinh Diem administration. Photos of his self-immolation were circulated widely across the world and brought attention to the policies of the Diem regime. Malcolm Browne won a Pulitzer Prize for his iconic photo of the monk's death, as did David Halberstam for his written account. After his death, his body was re-cremated, but his heart remained intact.
'Before closing my eyes to go to Buddha', wrote Quang Duc, 'I have the honour to present my words to President Diem, asking him to be kind and tolerant towards his people and enforce a policy of religious equality.' Thich Quang Duc act increased international pressure on Diem and led him to announce reforms with the intention of mollifying the Buddhists. The promised reforms were implemented either slowly or not at all, leading to a deterioration in the dispute. With protests continuing, the Special Forces loyal to Diem's brother, launched nationwide raids on Buddhist pagodas causing deaths and widespread damage.
Several Buddhist monks followed Thich Quang Duc example and burned themselves to death. Eventually, an Army coup toppled and killed Diem in November. The self-immolation is widely seen as the turning point of the Vietnamese Buddhist crisis which led to the change in regime.
Link: Thich Quang Duc Wiki
Links: Stefan Lux Wiki / Stefan Lux Speedy Notes
Dying Without Killing, History of Self-Immolations 1963–2002 (PDF) From Making Sense of Suicide Missions - Michael Biggs
Dying For A Cause By Michael Biggs
The Transnational Diffusion of Protest by Self-Immolation (PDF) By Michael Biggs, Department of Sociology, University of Oxford
Epidemiology Of Self-Immolation In The North-West Of Iran (PDF)
In this research, medical records of ninety eight cases who attempted suicide by self-immolation between 1998 and 2003 were studied.











